By Ian Manlulu, Logistics Operations Specialist
Resource planning is the ability to forecast requirements and develop a strategy to plan, allocate, and utilize the resources and employee competencies effectively.
In the fast-paced environment like warehouse operations that is operating 24/7, it is necessary that you strategically plan the needed resources to effectively perform at the desired level.
The Most Common Resources in Warehouse Operations
1. Manpower
This is the most essential resource in warehouse operations as this will directly affect the deliverables for each warehouse process. Manpower is the backbone of every operation consisting of various positions that can help run the warehouse process from receiving, storage, picking and packing to shipping (see overview of key warehouse processes).
2. Equipment
Equipment – these are commonly called material handling equipment (MHE) which includes the following:
Manual jack pallet
this are hand-operated trolley used to lift, move, and transport pallets within short distances by the order picker.
Battery Operated Forklift
Typically powered by battery, this industrial truck can be used to move and transport loads within the warehouse. This equipment is also used in unloading and loading palletized products into truck. Depending on the capacity, forklifts can carry load for an average of 3 tons.

Lifting Crane
These are typically installed to lift heavy objects that cannot be lifted by equipment. Normally, if there are forklifts operated by batteries, lifting cranes are installed to assist in safely changing the battery into the forklift unit.
Reach Truck
This is a type of forklift that handles the organizing of palletized products inside the warehouse storage. This are typically used in lifting palletized products to high racking storage location that can reach up to 7 meters height.
3. Other resources
These are the resources that are needed for the warehouse to operate. Examples of this are laptop, printers, office supplies, containers such as crates, pallets, and boxes etc.
Typical challenges that affect resource planning in a warehouse operation
Resource Planning Variables
Manpower attendance
One of the typical challenges in resource planning is the scheduling of manpower according to the need of the warehouse operations deliverables that are based on function per position.
Inconsistency of attendance of employees may vary on the different root causes. But the bottom line is that companies should be prepared in the event of unexpected absences for each critical role especially for those critical roles that are directly affecting the productivity of the operations.
It is important to have manpower pooling for the identified key positions such as Picker, Checker, Forklift Operator and Documentation staff to ensure that there is business continuity for warehouse operations.
There are two ways to develop this technique: long-term and short-term development.
- For the long term, Supervisors can identify employees with capabilities to learn multiple tasks and train them for succession so that when the need arises, they will be utilized as a backup for the role.
- Short-term development may be done by hiring seasonal skilled workers and using them to fill in the position as a temporary replacement.
Working hours per country
Around the world, the average working hours per week can range from 40 hours to 50 hours. The allowable working hours varies in different countries and can affect the resource planning on manpower scheduling.
With greater working hours, the manpower schedule can be planned according to the normal operations.
However, with the lesser working hours, Supervisors and Managers should determine if there are need for additional headcount to support the warehouse operations.
Equipment planning
Along with the manpower planning, should have corresponding equipment planning.
Ideally, there should be a 1:1 ratio of operator to the equipment such as forklift and reach truck. Plans to increase manpower shall mean an increase in resources like equipment.
For example, if there are additional operator during the peak season, there should also have necessary additional forklift units.
Natural Calamities
Sometimes, there are natural calamities that affect the employees and the whole organization like typhoon, floods, accidents etc.
When this happens, it is important to have employee profiling to be able to establish recovery team when there are delays in the operation due to majority of the employee are unable to report to work.
The call tree may include employee contact number, address, or proximity to the warehouse.
This call tree shall be the business continuity plan for the organization by contacting those employees that are near the warehouse site and can report to work.
Adapting and using the Warehouse Resource Planning Sheet
You can download the Warehouse Resource Planning Sheet further below!
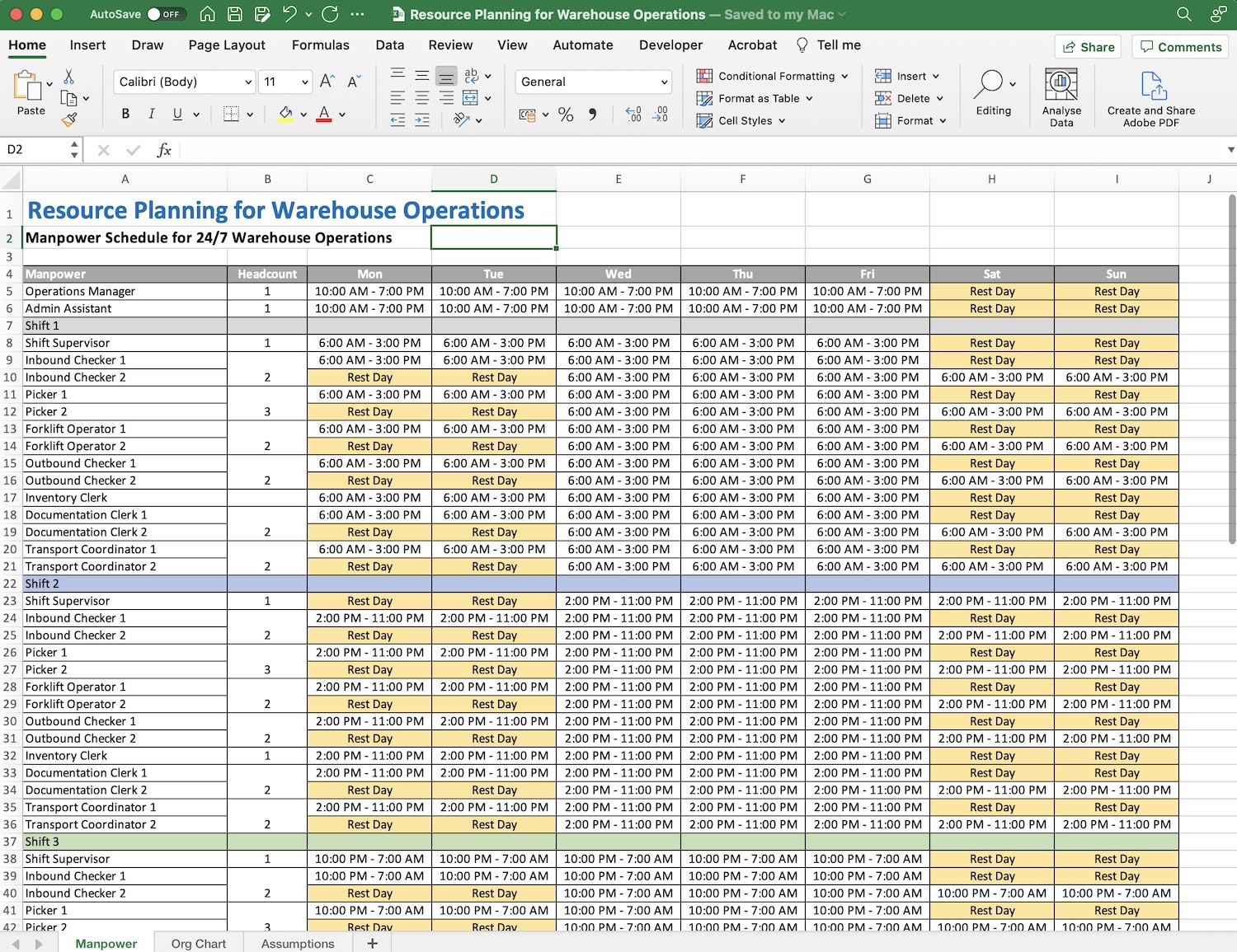
The number of headcounts in a warehouse operation varies on the volume of transactions and may differ based on the number of SKU or product being managed.
Typically, the core positions that are needed for a warehouse operation to function are forklift operator, checker, picker, documentation clerk, transport coordinator and inventory clerk. This are all the core positions that can run the warehouse operations. Generally, these are the positions given with high priority in filling up of the required headcount per shift to ensure that desired performance will be achieved.
It is also essential to have historical performance data from warehouse operations to identify the peak and lean days within a month. Identifying lean days and the busiest days of the week will help your manpower planning determine when and how many of the personnel can have their rest day and where and when to focus the skilled and productive employees.
Resource planning will be dependent on the complexity of the operations and the volume quantity of incoming and outgoing products to cater customer orders on-time.
The headcount per position will also be dependent on these elements. For small operations, roles and responsibilities may be integrated into one position or individual. And then eventually, branch out to different roles as the volume and the organization becomes bigger or warehouse operations are moved to a larger facility.
One example of this is when the inbound checker is trained and authorized to operate forklifts, they can transport the product they checked inside the warehouse.
Another example of this is the transport coordinator, which plans and coordinates to the truckers all product for delivery and at the same time prepares all documents corresponding to each truck. This kind of hybrid role can be exercised by small organizations to maximize their manpower.
Shift turn over should also be part of manpower schedule to give enough time for the workers to hand over pending task to the succeeding workers of the next shift. This will ensure that no task or activities are left behind and all pending tasks will be continued by the incoming shift.
Aside from turnover, another essential plan to do in scheduling manpower is the shift rotation of workers.
Shift rotation means that morning, night, and graveyard shift follows a cycle to move workers from one shift to another.
Schedule are typically have validity and may eventually be changed according to shift rotation plan of the Supervisors or Manager.
Tips on creating reliable resource plan for your warehouse
To be able to create a reliable resource plan, the following can be considered:
- Data or information of warehouse operations containing historical transactions and product volume are essential in planning resources in the operations. These can be used to identify trends to effectively plan manpower and resources. This can be the receiving volume in terms of quantity, number of pallets moved, order volume, and number of trucks to be loaded etc.
- Create manpower pooling for key positions. Key positions for warehouse operation consisting of forklift operator, picker, checker, documentation staff are the core group to operate effectively. Uncontrollable aspect of human resource is the attendance performance that may vary depending on the situation, to ensure continuous operations, there should be manpower pooling established.
- Plan Ahead. Identifying seasonal requirements can help companies accurately plan for the needed resources in the warehouse operation. This can give other departments like Human Resources to search and hire additional manpower needed to support high volume season. Warehouse operations can also prepare and train people so that they will be equipped with skills and be familiar with the warehouse layout when needed. Ideally, resource planning for peak season should be initiated three months prior.
- Balance your resources. Supervisors should have deep understanding on the capabilities and skills of each employee, so that when doing manpower schedules, the above average worker should be distributed in every shift. This method can be used to balance productivity, maintain desired performance, and prevent manpower exhaustion.
- Establish a call tree for each position and employee. It is essential to have contact numbers of each employee that are arrange according to their position so that when unexpected situation happens, they can be easily called and requested to report on duty. This call tree can also be used to contact each person if in case they do not show up in their assigned schedul

About the author
Ian Manlulu is a Logistics Operations specialist with over 12 years of experience in supply chain and warehouse management. He is a real expert in building efficient warehousing processes and possesses immense hands-on experience in the day-to-day management of large warehouses.